CPT Code 90839: Essential Billing Guide for Crisis Therapy [2025 Rules]
Understanding when — and how — to bill crisis CPT codes 90839 and 90840 is essential for accurate reimbursement and compliance in behavioral health. This guide explains exactly what qualifies as a crisis session, how the 30–74 minute and 75+ minute time thresholds work, when to add 90840, and what documentation payers require to support medical necessity. You’ll learn the core elements of a billable crisis intervention, common billing mistakes that lead to denials, and real-world examples to help you distinguish crisis codes from standard psychotherapy. Whether you’re billing Medicare, Medicaid, or commercial payers, this article provides clear, practical instruction to help you code crisis sessions confidently and correctly.

Racheal Morris, RHIT
Last Updated: December 11, 2025


What You'll Learn
-
What qualifies as a billable crisis session under CPT codes 90839 and 90840 — and how to distinguish true crisis interventions from routine psychotherapy.
-
Exact time requirements for crisis billing, including how the 30–74 minute rule works for 90839 and when to apply add-on code 90840 for extended sessions.
-
Documentation essentials that payers look for, including crisis assessments, mental status exams, start/stop times, safety planning, and medical-necessity justification.
-
How to avoid common billing errors that lead to denials, such as incorrect code pairing, insufficient documentation, and misuse of interactive complexity or standard therapy codes.
-
Real-world examples of when to bill crisis codes versus standard psychotherapy (90832/90834/90837) to ensure accurate, compliant claims.
-
Key payer rules for 2025, including Medicare reimbursement rates, commercial payer variations, and telehealth or after-hours considerations.
-
Best practices for clean claims, ensuring you receive appropriate reimbursement for high-intensity crisis intervention work.
Contents
- Crisis Therapy Billing Made Simple
- Recognizing a Billable Crisis Session
- Breaking Down CPT Code 90839
- How and When to Use CPT Code 90840
- Billing Rules and Time Thresholds Explained
- What to Include in Your Documentation
- Maximize Your Crisis Code Reimbursements
- How ICANotes Simplifies Crisis Documentation and Billing
- Bringing It All Together: Billing Crisis Codes Confidently and Correctly
- FAQs: Crisis CPT Codes
CPT code 90839 provides mental health providers with higher reimbursement rates for crisis therapy sessions that demand immediate intervention. When your clients face life-threatening circumstances or experience severe psychological distress, this specialized billing code ensures you receive appropriate compensation for emergency care. The 2025 Medicare rate for CPT code 90839 is $148.47 [21] — notably higher than standard 60-minute therapy sessions.
Crisis Therapy Billing Made Simple
CPT code 90839 covers your first 30-74 minutes of emergency intervention [9]. Sessions extending beyond 74 minutes qualify for add-on code 90840, which pays an additional $72.78 for each 30-minute increment [21]. This billing structure recognizes the intensive nature of crisis work and compensates you accordingly [8].
These crisis codes apply exclusively to patients requiring immediate, high-intensity interventions. You can report 90839 only once per day, though the therapy time doesn't need to be continuous. The codes are designed for clients experiencing genuine mental health emergencies — situations involving high distress and complex problems demanding urgent professional attention [4].
This guide shows you exactly when to use crisis codes, what qualifies as a billable crisis session, the required time thresholds, documentation requirements, and payer rules you need to maximize your reimbursements while delivering critical care.
Recognizing a Billable Crisis Session
Identifying whether your session qualifies for crisis code 90839 requires understanding specific clinical criteria that separate emergency interventions from routine therapy sessions.
What Counts as a Crisis Under CPT 90839
Official CPT guidelines define a billable crisis under 90839 as a presenting problem that is "typically life-threatening or complex and requires immediate attention to a patient in high distress" [2]. This represents the severe end of the crisis spectrum that most mental health professionals encounter.
The situation must demonstrate clear medical necessity requiring prompt intervention. You're looking for circumstances where patients experience severe psychological distress that significantly impairs functioning or threatens their safety or others' safety.
Your crisis therapy session must include these essential elements:
- Urgent assessment and history of the crisis state
- Mental status examination
- Development of a disposition plan
- Mobilization of resources to defuse the crisis and restore safety
- Implementation of interventions to minimize potential psychological trauma
Crisis therapy focuses on stabilizing patients experiencing acute psychological emergencies rather than addressing ongoing therapeutic goals.

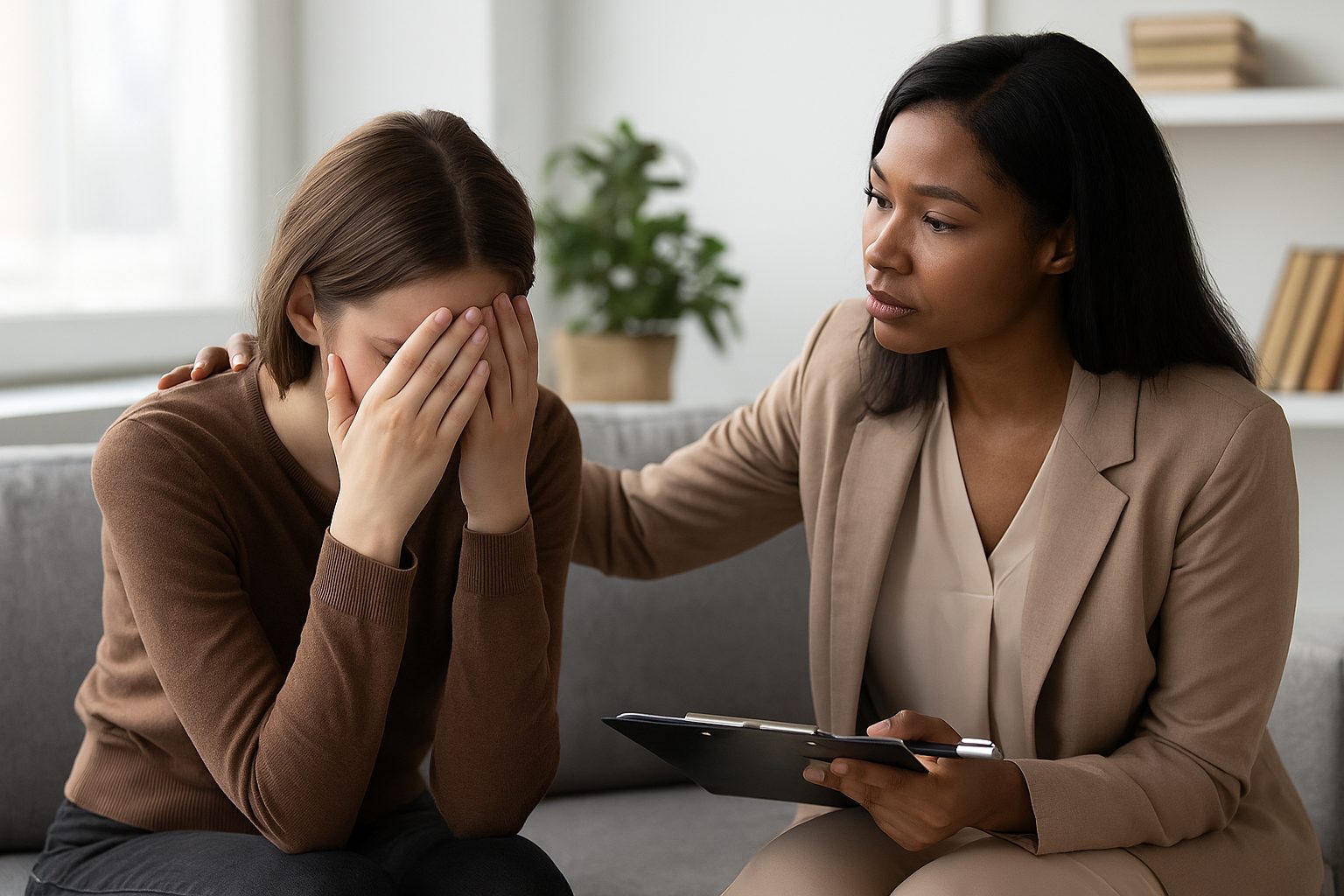
Clinical Examples: Suicidal Ideation, Panic Attacks, Trauma
Specific clinical scenarios clearly justify using CPT code 90839. These situations involve acute, severe symptoms demanding immediate intervention:
Suicidal ideation or intent: Active suicidal thoughts, plans, or recent attempts
Grave disability or disabling anxiety: Overwhelming panic attacks that pose safety risks
Acute psychological distress: Severe anxiety, psychosis, or other symptoms significantly affecting functioning
Behavioral emergencies: Patient behavior poses imminent risk to themselves or others, including self-harm or aggression [8]
Acute trauma response: Recent sexual assault, domestic violence, or sudden loss requiring immediate crisis intervention
Significant decompensation: Clinical deterioration that risks the patient's ability to remain at their current level of care
Consider a patient calling your office reporting overwhelming panic symptoms with potential self-harm risk, or someone arriving following a traumatic event in severe distress. These situations typically warrant crisis intervention coding.
When Not to Use Crisis Codes
Many therapy sessions involve distressing content but don't qualify for crisis codes. You cannot use 90839/90840 for:
- Regularly scheduled therapy appointments, even when patients discuss distressing content
- Sessions focused on ongoing therapeutic goals rather than emergency stabilization
- Situations where patients experience distress but remain functionally stable
- Standard intake evaluations (90791/90792)
- Regular psychotherapy sessions (90832, 90834, 90837)
You cannot bill crisis codes simultaneously with standard therapy codes or with interactive complexity (90785). Crisis codes inherently include the clinical complexity found in crisis management situations.
Documentation remains critical for justifying crisis code usage. Your notes must explicitly describe the crisis nature and severity, including precipitating events, risk assessments, and specific interventions. Without thorough documentation demonstrating true crisis circumstances, payers will deny your claims.
Before submitting CPT code 90839, verify the session genuinely addressed an urgent, high-risk situation requiring immediate intervention rather than routine therapeutic care.
Breaking Down CPT Code 90839

Understanding Crisis Code Mechanics
CPT code 90839 requires specific clinical and billing knowledge to use effectively. This specialized code works differently from standard therapy billing and carries unique requirements you need to understand.
CPT Code 90839 Description
CPT code 90839 represents "psychotherapy for crisis – first 60 minutes" of emergency mental health intervention. The code covers urgent assessment and history of a crisis state, mental status examination, and disposition planning [7]. Your crisis intervention services help reduce the patient's mental health crisis through focused, immediate interventions.
The primary service elements you must provide include:
- Urgent assessment and history of the crisis situation
- Mental status examination
- Resource mobilization to defuse the crisis
- Interventions designed to minimize potential psychological trauma
This code applies when patients present with life-threatening or highly complex problems requiring immediate professional attention. The service must address a genuine emergency rather than routine care, even when routine care involves distressing topics.
The time you bill under 90839 doesn't need to be continuous on the date of service. You can bill for crisis intervention provided across multiple interactions on the same day, provided they collectively meet the minimum time threshold.
Who Can Bill 90839
Medicare and most commercial insurers allow various mental health professionals to bill using the 90839 crisis code. Eligible providers include:
- Physicians (MDs and DOs)
- Clinical psychologists (CPs)
- Clinical social workers (CSWs)
- Clinical nurse specialists (CNSs)
- Nurse practitioners (NPs)
- Physician assistants (PAs)
- Certified nurse-midwives (CNMs)
- Marriage and Family Therapists (MFTs)
- Mental Health Counselors (MHCs)
Physicians and certain non-physician practitioners can bill for services provided by auxiliary personnel (such as peer support specialists) "incident to" their professional services, provided they maintain appropriate supervision and comply with state laws.
Crisis sessions can be delivered virtually anywhere — outpatient offices, patients' homes, hospitals, or skilled nursing facilities – as long as you practice within your scope as defined by state law.
How 90839 Differs From Standard Therapy Codes
CPT code 90839 operates under different rules than standard psychotherapy codes:
Purpose and Application 90839 is exclusively for emergency situations requiring urgent intervention, whereas standard therapy codes (90832, 90834, 90837) are used for routine scheduled care [8]. The presenting problem must typically be life-threatening or require immediate attention to a patient in high distress.
Reimbursement Structure
Payment for psychotherapy crisis services is typically set at 150% of the fee schedule amount for services furnished in non-facility settings. This higher reimbursement reflects the intensive, specialized nature of crisis intervention.
Billing Restrictions: Crisis codes cannot be billed simultaneously with standard psychotherapy codes or initial evaluations. You cannot use 90839/90840 in conjunction with:
- 90791 and 90792 (initial evaluations)
- 90832, 90834, and 90837 (standard psychotherapy)
- 90785 (interactive complexity)
Time Flexibility: Standard therapy codes have strict time thresholds (16-37 minutes for 90832, 38-52 minutes for 90834, etc.), while 90839 covers a broader time range of 30-74 minutes. This flexibility acknowledges the unpredictable nature of crisis situations.
Documentation Requirements: Your crisis code notes must explicitly demonstrate the emergent nature of the situation and document specific crisis interventions, whereas standard therapy documentation focuses more on progress toward treatment goals.
Free 2026 Billing Guide for Mental Health Providers
Clean claims. Correct coding. Fewer denials.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to bill accurately, reduce denials, and protect your revenue. Download your copy and get the tools you need to streamline billing and boost reimbursement.
How and When to Use CPT Code 90840
When crisis therapy extends beyond 74 minutes, CPT code 90840 becomes your key to additional reimbursement for lengthy crisis interventions. This specialized add-on code works exclusively with 90839 to ensure you receive proper compensation for extended emergency care.
Extended Crisis Sessions = Higher Pay
CPT code 90840 represents "psychotherapy for crisis; each additional 30 minutes". Unlike standard therapy codes, 90840 is strictly an add-on code that cannot stand alone. You must always bill it alongside the primary crisis code 90839.
The purpose is simple, 90840 allows you to bill for extended crisis work beyond the initial session. Both codes reflect the same crisis therapy service but cover different time segments within a single intervention.
Crisis situations often demand longer interventions than standard therapy sessions. During extended sessions, you continue delivering the same crisis services — urgent assessment, mental status examination, and intensive intervention — that began in the initial segment [10].
Time Thresholds You Need to Know
Your crisis session must extend beyond 74 minutes for 90840 to apply. The time parameters work as follows:
- CPT code 90839 covers the first 30-74 minutes of crisis intervention
- CPT code 90840 applies for each additional 30-minute increment beyond 74 minutes
To properly bill the add-on code, your session must reach at least 75 minutes of total face-to-face time. The client needs to be seen for a minimum of 15 additional minutes beyond the initial 74 minutes for the time to round up to the next unit of 90840.
Some documentation lists the threshold as 60 minutes rather than 74 minutes [2] [10] [7]. Different payers may have varying interpretations of time requirements. Most providers follow the 30-74 minute threshold for 90839 to align with CPT guidelines.
Billing Multiple Units for Maximum Reimbursement
You can bill multiple 90840 units for exceptionally long crisis sessions. Each unit represents an additional 30-minute increment [11]. Here's how billing works:
Crisis Session Duration:
- 30-74 minutes: Bill only 90839
- 75-104 minutes: Bill 90839 + one unit of 90840
- 105-134 minutes: Bill 90839 + two units of 90840
- 135+ minutes: Bill 90839 + three (or more) units of 90840
Practical Examples:
- 30-minute crisis session: Use only 90839 (minimum time)
- 74-minute session: Use only 90839 (maximum before add-on needed)
- 75-minute session: Bill 90839 + one unit of 90840
- 104-minute session: Bill 90839 + one unit of 90840 (maximum before second add-on)
- 105-minute session: Bill 90839 + two units of 90840
Remember that crisis services don't need to be continuous on the same date. You must document the total face-to-face time spent with the patient or family. The provider must devote immediate attention to the patient for the entire billed duration.
When using CPT code 90840, no additional documentation is required beyond what's needed for 90839. Your clinical note should clearly justify why crisis intervention was necessary and detail the specific actions taken during those additional 30-minute increments.
Billing Rules and Time Thresholds Explained
Time-based billing rules determine your reimbursement success with crisis therapy codes. Master these precise thresholds for CPT code 90839 and add-on code 90840 to ensure accurate billing and optimal payment for your crisis intervention services.
90839: 30 to 74 minutes
CPT code 90839 applies to crisis sessions lasting 30-74 minutes [12]. The 30-minute minimum establishes your baseline requirement for billing this code. Sessions shorter than 30 minutes cannot use crisis codes — consider standard psychotherapy codes like 90832 (16-37 minutes) for brief crisis-like interactions.
The time providing crisis services doesn't need to be continuous on the same date. You can bill for multiple crisis interactions with the same patient on a single day, provided they collectively meet the 30-74 minute range.
Your documentation must include exact start and stop times to justify the time-based billing. You must devote immediate attention to the patient for the entire reported duration.
90840: 75+ minutes and beyond
When your crisis session extends beyond 74 minutes, add-on code 90840 applies. This code represents each additional 30 minutes of crisis intervention beyond the initial time frame. Follow these specific billing rules:
- 75-104 minutes: Bill 90839 + one unit of 90840 [13]
- 105-134 minutes: Bill 90839 + two units of 90840
- 135+ minutes: Add another unit of 90840 for each additional 30-minute increment
The client needs a minimum of 15 additional minutes beyond the 74-minute threshold to round up to the next billable unit of 90840. At 75 minutes, you can add the first unit of the add-on code.
Remember: 90840 is an add-on code that can only be used with 90839. It cannot stand alone on claims or pair with other psychotherapy codes.
These two crisis codes remain the only crisis codes reimbursable by Medicare as of 2020. Various Medicaid programs use different HCPCS codes for crisis services (H0030, H2011, S9484, S9485, and T2034) [12].
Sample Billing Scenarios
Here are practical examples to clarify these billing rules:
- 10-minute emergency call: Cannot use crisis codes. Use 90832 or 90833 (when provided with E/M services)
- 45-minute crisis session: Bill only 90839
- 74-minute session: Bill only 90839
- 90-minute crisis intervention: Bill 90839 + one unit of 90840
- 110-minute extended crisis: Bill 90839 + two units of 90840
Each health plan may limit how many 90840 units they cover per day, month, or year. While 90839 pays similarly to 90837 (60-minute psychotherapy), the ability to add 90840 for longer sessions creates a reimbursement advantage.
These time-based billing rules ensure fair compensation for your intensive crisis intervention work while maintaining billing consistency and compliance.
What to Include in Your Documentation
Proper Documentation Ensures Maximum Reimbursement
Insurance companies scrutinize crisis session claims closely. Your documentation must clearly demonstrate the emergency nature of the intervention and justify why crisis codes apply instead of standard therapy billing.
Crisis Assessment and Mental Status Exam
Your documentation must clearly describe the crisis situation that necessitated urgent intervention. Differentiate this encounter from routine therapy by detailing the nature and severity of the crisis [8]. Include a comprehensive mental status examination covering the patient's:
- Appearance and behavior
- Speech patterns
- Mood and affect
- Thought processes and content
- Cognitive functioning
- Orientation status
Connect your assessment to the appropriate ICD-10-CM diagnosis code that justifies the medical necessity for crisis intervention. Your notes should explain why this situation required immediate, high-intensity intervention rather than standard care.
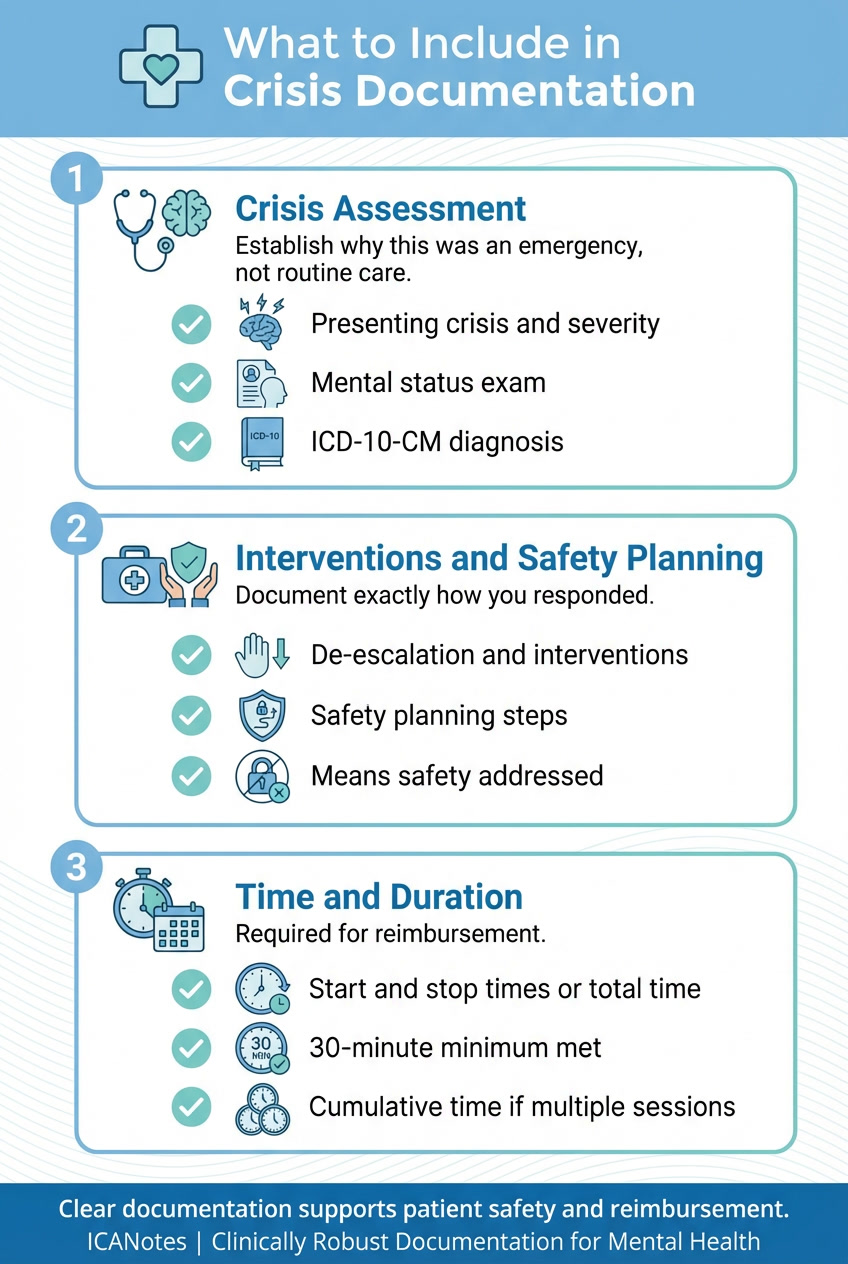
Interventions and Safety Planning
Your documentation must specifically outline the crisis interventions implemented during the session [14]. Detail exactly how you responded to the crisis, including:
- De-escalation techniques employed
- Resources mobilized to stabilize the situation
- Therapeutic interventions utilized
- Patient's response to these interventions
Document safety planning elements including warning signs, internal coping strategies, social contacts for distraction, family/friend supports, professional resources, and steps to secure the environment. For high-risk cases, document your assessment of access to lethal means and actions taken to limit such access [15].
Start/Stop Times and Session Duration
Precise time documentation is critical. You must record either the start and stop times or the total face-to-face time for every crisis session. Without documented time, insurance companies consider the service undelivered [1].
For sessions with multiple crisis interactions on the same day, document each segment's timing while ensuring the cumulative time meets the minimum 30-minute threshold. When billing multiple units of 90840, your documentation must support that the entire duration was necessary for the patient's care.
Comprehensive documentation not only satisfies reimbursement requirements but also establishes the medical necessity of crisis intervention. Accurate time tracking, detailed assessment notes, and thorough intervention documentation create a complete clinical record that supports both optimal patient care and appropriate compensation for your intensive services.
Maximize Your Crisis Code Reimbursements
Getting paid properly for crisis intervention work requires understanding current rates and avoiding common billing errors. Smart billing practices reduce claim denials and ensure you receive appropriate compensation for these intensive sessions.
2025 Crisis Code Payment Rates
Medicare reimburses CPT code 90839 at $148.47 for 2025, up from $144.07 in 2024 [3]. The add-on code 90840 pays $72.78 per 30-minute increment [16]. Medicare pays 150% of the standard fee schedule amount for crisis services in non-facility settings [17], recognizing the urgent nature of this work.
Commercial payers offer varying rates. United Healthcare pays approximately $150.12 for 90839 under standard contracts and $130.09 under value-based arrangements [3]. With the ET modifier for emergency services, reimbursement increases substantially to $214.04 [3]. National averages across major insurers range from $140.95 to $210.07 [18].
Billing Errors That Cause Denials
Avoid these common mistakes that trigger automatic claim denials:
- Billing 90840 without the primary 90839 code [19]
- Reporting sessions under 30 minutes with crisis codes [3]
- Using crisis codes for routine therapy sessions [3]
- Submitting claims without clear crisis documentation [19]
- Including family therapy time instead of direct patient contact [19]
- Billing crisis codes with standard therapy codes on the same day [9]
Incomplete documentation remains the top reason for denials. Without detailed assessment notes, mental status exams, and disposition plans, insurers will reject your claims [17].
Telehealth and After-Hours Billing
For telehealth crisis sessions, use Place of Service code 02 for facility-based patients or POS 10 for home-based patients [6]. Add modifier 95 for live video sessions or 93 for audio-only when allowed [6].
After-hours services qualify for additional codes:
- 99050 for services during closed office hours [3]
- 99051 for scheduled evening, weekend, or holiday appointments [3]
Document the connection method, patient location, and consent for telehealth services [6]. After-hours billing requires clearly posted office hours in your practice materials [3].
How ICANotes Simplifies Crisis Documentation and Billing
Accurate documentation is essential when billing crisis psychotherapy services, and using the right EHR can dramatically reduce errors and denials. ICANotes is purpose-built for behavioral health clinicians and includes structured workflows that support every requirement of CPT codes 90839 and 90840.
With ICANotes, clinicians can document crisis encounters using pre-built crisis note content templates that prompt the inclusion of required elements such as risk assessments, mental status exams, crisis intervention strategies, and disposition planning. Built-in time tracking allows you to record start/stop times or total duration automatically, ensuring your notes support time-based billing thresholds for both the initial 30–74 minutes and any add-on units for extended sessions.
ICANotes also helps prevent billing mistakes by blocking incompatible code combinations and guiding users through payer-compliant documentation fields. Whether you’re providing care in person, via telehealth, or during after-hours, ICANotes makes it easier to capture the clinical detail needed to justify medical necessity and submit clean, accurate claims.
Start your free trial of ICANotes to streamline crisis documentation and reduce billing errors.
Start Your 30-Day Free Trial
Experience the most intuitive, clinically robust EHR designed for behavioral health professionals, built to streamline documentation, improve compliance, and enhance patient care.
- Complete Notes in Minutes - Purpose-built for behavioral health charting
- Always Audit-Ready – Structured documentation that meets payer requirements
- Keep Your Schedule Full – Automated reminders reduce costly no-shows
- Engage Clients Seamlessly – Secure portal for forms, messages, and payments
- HIPAA-Compliant Telehealth built into your workflow
Complete Notes in Minutes – Purpose-built for behavioral health charting
Always Audit-Ready – Structured documentation that meets payer requirements
Keep Your Schedule Full – Automated reminders reduce costly no-shows
Engage Clients Seamlessly – Secure portal for forms, messages, and payments
HIPAA-Compliant Telehealth built into your workflow
Bringing It All Together: Billing Crisis Codes Confidently and Correctly
CPT codes 90839 and 90840 give you the tools to receive proper compensation for life-saving crisis intervention work. These specialized codes recognize the intensive nature of emergency mental health care and pay you accordingly.
Crisis therapy billing comes down to three essential requirements. The situation must involve genuine crisis circumstances requiring immediate intervention. Your session must meet the time thresholds: 30-74 minutes for 90839, with 90840 adding coverage for longer interventions. Most importantly, your documentation must clearly demonstrate the emergency nature of the situation and the specific interventions you provided.
The 2025 reimbursement rates make crisis coding financially worthwhile. Medicare pays $148.47 for 90839 and $72.78 for each additional 30-minute increment with 90840. Commercial insurers typically follow similar rates, often paying even more for emergency services.
Crisis codes cannot be combined with standard therapy codes on the same day. You must document why the situation required emergency intervention rather than routine care. The distinction matters for both clinical and billing purposes.
When you master these billing guidelines, you ensure proper reimbursement while providing critical care during your patients' most vulnerable moments. Crisis therapy represents some of your most challenging and important clinical work. Proper coding simply ensures this essential work receives the recognition and compensation it deserves.
Focus on delivering quality crisis care. The billing follows naturally when you understand these straightforward rules.
Frequently Asked Questions: Crisis CPT Codes
Related Posts
About the Author
Racheal Morris is a certified medical coder and biller with over 15 years of experience in behavioral health settings. As an RCM Account Manager at ICANotes, she ensures that our customers' billing, claims, and reimbursement processes run smoothly, efficiently, and compliantly — and that revenue is maximized with minimal delays or denials.






