Blog > Documentation > Psychiatric Nursing Notes: Examples & Best Practices
Psychiatric Nursing Notes: What to Include, Examples, and Best Practices
Psychiatric nursing notes are a critical component of mental health documentation, supporting continuity of care, clinical decision-making, and regulatory compliance. This guide explains what psych nursing notes should include, provides practical psychiatric nursing notes examples, and outlines best practices for writing clear, defensible mental health nursing notes across inpatient and outpatient settings.

Last Updated: December 30, 2025

What Are Psychiatric Nursing Notes?
Psychiatric nursing notes (also called psych nursing notes or mental health nursing notes) are shift-level clinical records written by nurses that describe:
-
The patient’s current mental and behavioral status
-
Nursing interventions provided
-
Response to treatment
-
Risk and safety concerns
-
Any changes in care or plan
These notes form part of the official medical record and are often used in care coordination, audits, and legal documentation.
Why Psychiatric Nursing Notes Matter in Mental Health Care
Psychiatric nursing notes play a critical role in the delivery of safe, effective, and coordinated mental health care. More than a record of tasks completed during a shift, psychiatric nursing notes document clinical judgment, patient status, and risk, helping ensure continuity of care across providers and settings.
In psychiatric and behavioral health environments — where symptoms can fluctuate rapidly and safety considerations are central — clear, consistent documentation allows the care team to understand what the patient is experiencing, how they are responding to treatment, and what interventions are most effective. Well-written psych nursing notes support informed clinical decision-making during handoffs, rounds, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
From a compliance perspective, mental health nursing notes help demonstrate medical necessity, adherence to treatment plans, and appropriate monitoring of risk factors such as suicidal ideation, aggression, or medication side effects. These notes are frequently reviewed during audits, utilization reviews, and legal inquiries, making accuracy and objectivity essential.
Psychiatric nursing notes also protect both patients and clinicians. By clearly documenting observations, interventions, and patient responses, nurses create a defensible clinical record that reflects professional standards of care. Over time, consistent documentation supports trend analysis, treatment planning, and quality improvement — ultimately contributing to better outcomes for individuals receiving mental health services.
10 Essential Components of Psychiatric Nursing Notes
Effective psychiatric nursing notes provide a clear, objective snapshot of a patient’s mental and behavioral status during a specific shift or encounter, while also documenting the nurse’s clinical judgment and interventions. Psych nursing notes are part of the legal medical record and must balance thoroughness with clarity, relevance, and timeliness. Each entry should communicate what was observed, what actions were taken, how the patient responded, and any safety considerations that influenced care decisions.
Strong mental health nursing notes focus on clinically meaningful information that supports continuity of care across providers, protects patient safety, and demonstrates adherence to the treatment plan. By consistently including the core elements outlined below, psychiatric nurses can create documentation that is defensible in audits, useful during handoffs, and reflective of professional standards — without becoming overly verbose or duplicative. Well-structured psychiatric nursing notes help ensure that critical details are easy to locate, interpret, and act upon in fast-paced behavioral health settings.
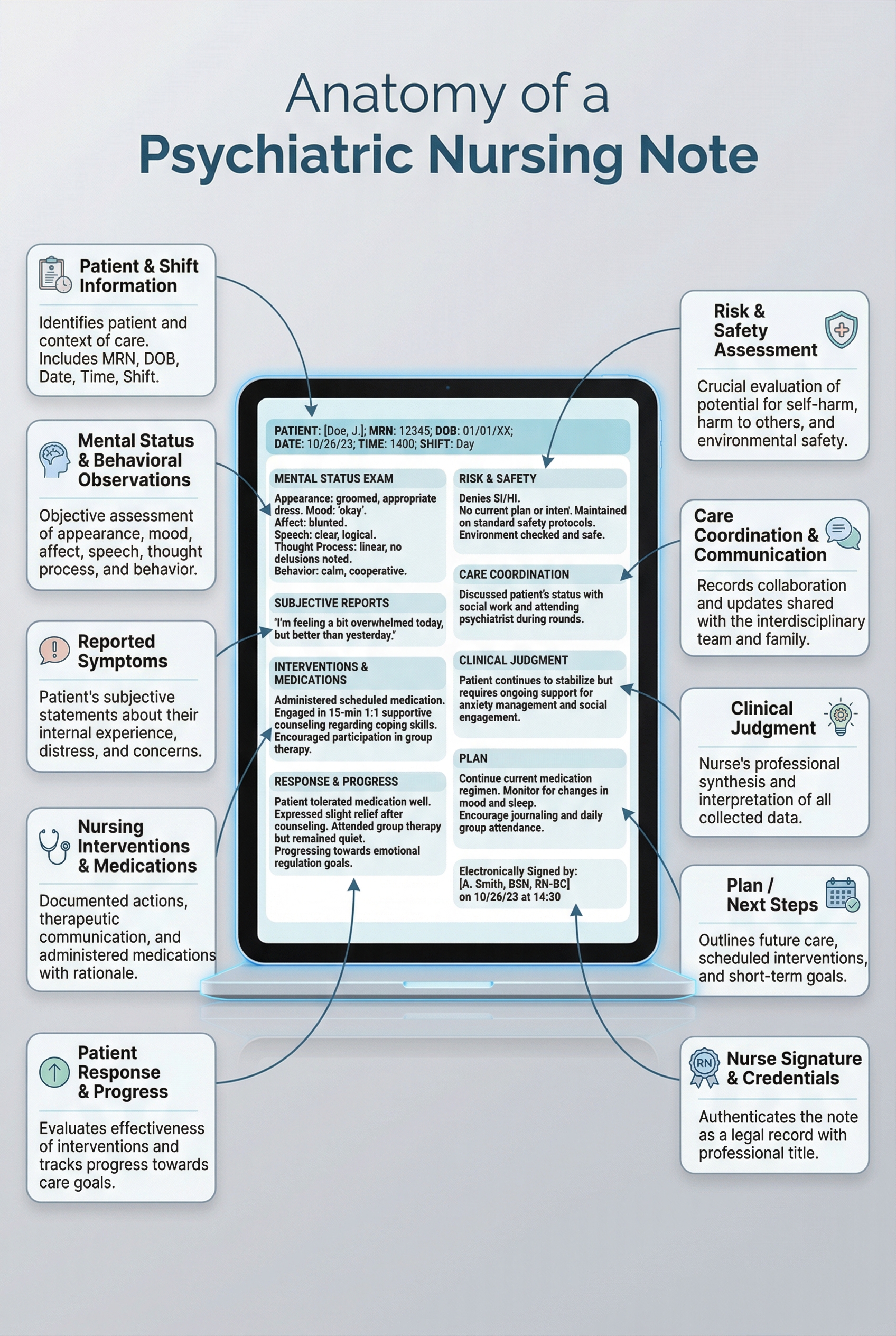
1. Patient Identifiers and Shift Information
Begin each psychiatric nursing note with clear identifying and contextual information. This includes the patient’s name or medical record number, date and time of the note, care setting, and your credentials. Accurate identifiers ensure continuity across shifts and reduce the risk of documentation errors in fast-paced behavioral health environments.
Example:
John Doe, MR#123456 | RN | 08/12/2025 | 07:00–15:30
2. Mental Status, Behavioral Observations, and Vital Signs
Document objective observations related to the patient’s mental status and behavior. This may include appearance, level of alertness, mood and affect, speech, thought process, eye contact, motor activity, and engagement with staff or peers. Focusing on observable behaviors strengthens the clinical reliability of mental health nursing notes and reduces subjective interpretation. When clinically indicated, this section may also include vital signs relevant to psychiatric stability, medication monitoring, or safety assessment.
Example:
Patient alert and oriented ×3; mood anxious with congruent affect; speech clear and coherent.
Vitals stable: BP 118/72, HR 76, RR 16, SpO₂ 98% on room air; no signs of acute distress observed.
3. Reported Symptoms and Objective Findings
Include relevant symptoms reported by the patient, such as anxiety, hallucinations, sleep disturbance, or mood changes, alongside any objective findings. When appropriate, use direct quotes to accurately capture the patient’s experience. This section helps establish clinical context and supports ongoing assessment of symptom trends.
Example:
Patient reports increased anxiety overnight and difficulty sleeping; pacing observed during morning hours.
4. Nursing Interventions and Medications
Clearly document nursing interventions provided during the shift, including medication administration, patient education, de-escalation efforts, coping skills coaching, or environmental modifications. For medications, note administration details and any observed or reported side effects. This section demonstrates active nursing care and adherence to treatment protocols.
Example:
Provided grounding techniques and supportive listening; administered scheduled sertraline per MAR with no adverse effects noted.
5. Patient Response and Progress
Describe how the patient responded to interventions, treatments, or medications. This may include changes in mood, behavior, participation, or symptom intensity. When possible, note measurable outcomes (for example, changes in anxiety ratings or engagement level). Tracking response over time supports treatment planning and interdisciplinary communication.
Example:
Patient engaged in coping exercise and reported anxiety decreased from 7/10 to 4/10.
6. Risk, Safety, and Observation Level
Document current safety considerations, including suicidal or homicidal ideation, self-harm risk, aggression, elopement risk, or changes in observation level. Include both patient statements and clinical observations. Clear risk documentation is a critical component of psychiatric nursing notes and is often closely reviewed in audits and legal inquiries.
Example:
Denies suicidal or homicidal ideation; no plan or intent expressed; continued on Q15 safety checks.
7. Communication With the Care Team
Note any significant communication with psychiatrists, advanced practice providers, therapists, or other members of the care team. This may include updates shared during rounds, notifications of symptom changes, or coordination related to medications or safety planning. This section supports continuity and collaborative care.
Example:
Updated psychiatrist during rounds regarding increased anxiety and sleep disruption.
8. Clinical Judgment and Rationale
When relevant, briefly document the clinical reasoning behind key nursing decisions, such as increased monitoring, provider notification, or intervention selection. This demonstrates professional judgment and helps contextualize care decisions for other clinicians reviewing the record.
Example:
Increased monitoring implemented due to escalating agitation observed earlier in the shift.
9. Alignment With the Treatment Plan
Connect observations and interventions to the patient’s established treatment goals or plan of care. This reinforces medical necessity and shows how daily nursing care supports broader therapeutic objectives. Alignment with the treatment plan is especially important for utilization review and compliance purposes.
Example:
Interventions focused on anxiety management in alignment with current treatment goals.
10. Signature and Credentials
Conclude the note with your full name, professional credentials, and the date and time of entry. Proper authentication ensures accountability and confirms the note as a complete, official part of the medical record.
Example:
Jane Smith, RN | 12/30/2025 | 15:45
Psych Nursing Notes Examples
The examples below illustrate how clear, concise psychiatric nursing notes document clinical observations, nursing interventions, patient response, and safety considerations in real-world mental health settings. All examples are illustrative and should be adapted to organizational policies, scope of practice, and patient-specific needs.
Date/Time: 12/30/2025 | 0700–1530 Clinician: RN
Presentation/MSE: Alert and oriented ×3. Mood anxious; affect congruent. Speech normal rate/volume. Thought process linear; denies AVH during shift.
Subjective: “I feel on edge and keep replaying what happened.”
Interventions: Provided supportive listening and coached grounding (5-4-3-2-1). Encouraged hydration and group participation. Administered scheduled meds per MAR; monitored for side effects.
Response/Progress: Participated in group with prompting; reported anxiety decreased from 7/10 to 4/10 after grounding.
Risk/Safety: Denies SI/HI; no plan/intent. Continued Q15 safety checks per protocol. No behavioral incidents.
Plan: Continue coping skills reinforcement; communicate anxiety trend to provider during rounds.
Date/Time: 12/30/2025 | 10:00 AM Clinician: RN
Presentation/MSE: Calm, cooperative, engaged. Affect appropriate. Thought content without delusions noted. Insight fair. Judgment intact.
Patient Report: “I missed two doses this week because I ran out.” Sleep improved; appetite stable.
Interventions: Reviewed medication adherence barriers and refill plan; provided education on missed-dose guidance per clinic protocol. Reinforced safety plan and coping strategy use.
Response/Progress: Patient verbalized understanding and agreed to pharmacy pickup today; identified one support person to call if symptoms escalate.
Risk/Safety: Denies SI/HI; no acute safety concerns. Advised to contact crisis services/911 for emergent needs per standard instructions.

Brief Examples of Psychiatric Nursing Notes
Psych Nursing Notes Examples – Inpatient Setting
Example 1: Patient alert and oriented ×3. Mood anxious; affect congruent. Reported intrusive thoughts overnight but denies SI/HI. Participated in group therapy with prompting. Administered scheduled medications; no adverse effects noted. Continues on Q15 safety checks.
Example 2: Patient reports fewer hallucinations today; mood stable. Participated in group therapy. Administered scheduled meds, no side effects. Denies SI/HI. Continued level 1 observations.
Mental Health Nursing Notes Examples – Outpatient / Community Setting
Example 1: Patient arrived on time, cooperative, and engaged. Speech clear and goal-directed. Reviewed medication adherence and reinforced coping strategies. No acute safety concerns. Follow-up scheduled for next visit.
Example 2: Conducted mental status check; patient calm, coherent. Reinforced safety plan. Discussed barriers to medication adherence. Patient agreed to follow-up in one week.
Access Our Sample Notes Library
Get instant access to our full library of sample behavioral health notes, including Initial Evaluations, Progress Notes, Treatment Plans, and Discharge Summaries. We have note samples for psychiatry, therapy, case management, PRP, substance abuse, group therapy, couples therapy, and more!

Best Practices for Writing Psychiatric Nursing Notes
Writing effective psychiatric nursing notes requires balancing clinical detail with clarity, objectivity, and efficiency. Because psych nursing notes are reviewed by multiple stakeholders — including providers, auditors, and legal teams — best practices focus on documenting what was observed, what actions were taken, and how the patient responded, rather than assumptions or interpretations. Consistent, well-structured mental health nursing notes support safe care transitions, reduce miscommunication across shifts, and create a defensible clinical record that reflects professional standards of psychiatric nursing practice.
FAQ: Psychiatric Nursing Notes
How ICANotes Helps Nurses Write Better Psych Nursing Notes
Psychiatric nurses often have to document quickly without sacrificing clinical quality, compliance, or clarity for the rest of the care team. ICANotes is designed to support behavioral health workflows by making psych nursing notes easier to complete, more consistent, and more defensible.
Built-in structure so nothing important gets missed
ICANotes guides nurses through the core components of strong psychiatric nursing notes — including mental status observations, interventions, safety/risk considerations, response to care, and next steps — so documentation stays organized and clinically complete, even during busy shifts.
Faster charting with time-saving note workflows
With point-and-click documentation and smart prompts, nurses can capture clinically relevant details efficiently without having to type lengthy narratives. This helps reduce charting time while still producing clear, professional mental health nursing notes.
Consistency across shifts and team members
Standardized formats help keep notes consistent from nurse to nurse, which improves continuity during handoffs and makes it easier for providers to quickly interpret the patient’s status, progress, and safety needs.
Supports risk and safety documentation
In behavioral health settings, risk documentation is critical. ICANotes makes it easier to document items like observation level, SI/HI status, behavioral escalation, and safety planning in a clear, repeatable way — supporting safer care and stronger audit readiness.
Better alignment with treatment plans and interdisciplinary care
ICANotes helps connect nursing documentation to the broader plan of care. When nursing interventions and patient responses are documented in a structured way, the full care team can more easily coordinate treatment and track progress over time.
Cleaner, more defensible notes for compliance and review
Clear structure, objective language, and complete documentation support medical necessity and reduce ambiguity. That’s especially valuable when notes are reviewed for quality, utilization management, audits, or legal purposes.
Bottom line: ICANotes helps psychiatric nurses produce high-quality psychiatric nursing notes that are faster to write, easier to read, and more supportive of safe, coordinated mental health care.
Book a Demo and see how ICANotes can help make psychiatric nursing notes easier and more consistent.
Schedule a Demo Today!
Experience the most intuitive, clinically robust EHR designed for behavioral health professionals, built to streamline documentation, improve compliance, and enhance patient care.
- Complete Notes in Minutes - Purpose-built for behavioral health charting
- Always Audit-Ready – Structured documentation that meets payer requirements
- Keep Your Schedule Full – Automated reminders reduce costly no-shows
- Engage Clients Seamlessly – Secure portal for forms, messages, and payments
- HIPAA-Compliant Telehealth built into your workflow
Complete Notes in Minutes – Purpose-built for behavioral health charting
Always Audit-Ready – Structured documentation that meets payer requirements
Keep Your Schedule Full – Automated reminders reduce costly no-shows
Engage Clients Seamlessly – Secure portal for forms, messages, and payments
HIPAA-Compliant Telehealth built into your workflow
Related Posts
About the Author
Dr. October Boyles is a behavioral health expert and clinical leader with extensive expertise in nursing, compliance, and healthcare operations. With a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) and advanced degrees in nursing, she specializes in evidence-based practices, EHR optimization, and improving outcomes in behavioral health settings. Dr. Boyles is passionate about empowering clinicians with the tools and strategies needed to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care.








